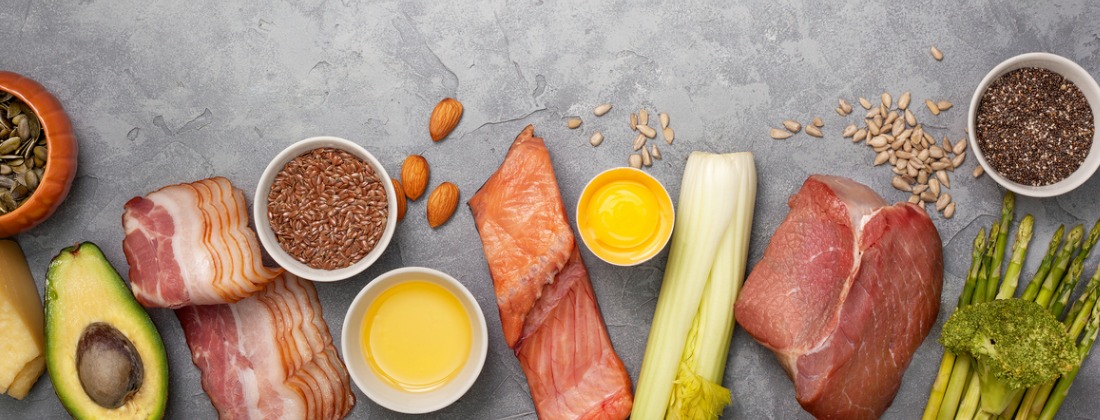
What is ‘keto’?
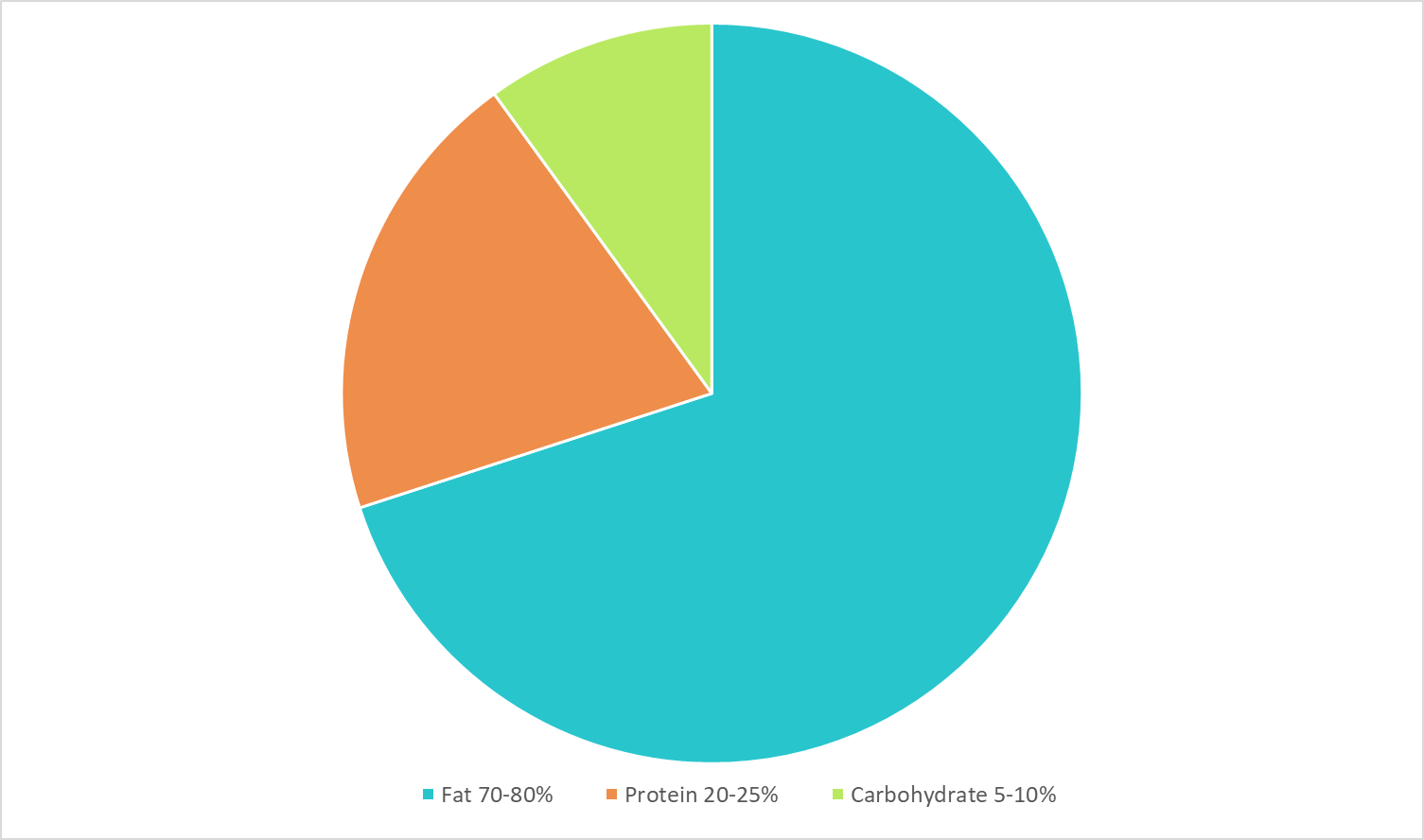
A standard ketogenic diet refers to a way of eating that is low in carbohydrates, high in fat, with adequate protein. Instead of burning glycogen (stored glucose), your body will burn energy from the fat you're eating and the fat you have stored. Fat provides more than double the energy when burned than protein or carbohydrates. Ketones are produced as a result of the body metabolising fat and are a very efficient source of fuel for the brain and body. A ketogenic diet is designed to put the body into mild nutritional ketosis, where it uses ketones to power cells for energy. For most people, that will mean a diet that consists of approximately 70-80% fat, 20-25% protein, and 5-10% carbohydrates.
People often are surprised at the high amount of fat that’s consumed. Yes, that means you will become very familiar with avocado and coconuts, as well as many other foods! If you have a very physical job or do a lot of exercise, you should consult an expert of the ketogenic diet in order to guide you on the right amount of carbohydrates for you, but typically, there is no more than about 50 grams of carbohydrates on a standard ketogenic diet. The amount of carbohydrate can increase depending on the needs of the individual.
Should you try going ‘Keto’?
Keto is being well researched around the world, including in New Zealand at AUT by experts in the Low Carb High Fat (LCHF) area. A ketogenic diet has been shown to support healthy weight management and balanced blood sugars without leaving you feeling starved or like you’re missing out on food. Calorie restrictive diets often make people feel hungry and cause cravings, but because there is a lot of healthy fats consumed, people feel full and satisfied. This helps maintain a healthier way of eating in the longer term. As well as supporting healthy weight management, a ketogenic state can also support mental performance, healthy hormones, energy, and optimal physical performance.
Foods to avoid:
- The carbohydrates most commonly avoided are those found in grains, rice, potato, lollies, flours, bread, crackers, chips.
- Processed foods, sugary drinks
- Fruit except for small portions of berries
- Low-fat foods
- Be aware of alcohol. Beer and wine have higher amounts of carbohydrates than spirits, and mixers tend to be high in sugar too, so soda water is an option.
Foods to include:
- Vegetables. Eat plenty of green, purple, orange, yellow, red vegetables. Limit consumption of starchy root vegetables to small portions.
- Fat! Avocado, coconuts, meat (with skin), eggs, butter, cheese, cream, full-fat dairy, nuts and seeds, olive oil, hemp seed oil, fish, and seafood
- Herbs and spices are great to include for flavour-full dishes
- Small portions of berries
- It’s really important to keep water intake adequate to at least 30ml per kilogram of weight per day, and more with exercise.
Keto supplements?
These are also known as exogenous ketones. They are used to support you into ketosis faster by providing ketones that are usable immediately for fuel. Taking these supplements can be dehydrating to the body, so make sure you drink lots of water. The most common example of an exogenous ketone supplement is MCT oil, the medium-chain triglycerides usually sourced from coconut oil.
What about the Keto-flu?
In the first few days, as your body adjusts to a different fuel, there can be side effects that feel similar to the flu – low energy, brain fog, and discomfort in the digestive system. It’s best to just be aware of these, rest, drink plenty of water, and know that it will only last a day or two. You can also increase the amount of salt on your food during these first few days as well to assist the symptoms. Including electrolytes in your diet can also help to keep you hydrated.
Who shouldn’t try it?
The keto diet has been found to be safe in research and is generally defined as low levels of ketones in the blood (0.5 – 1.5 mmol/L), so should be a helpful way to eat for many people, including diabetics. Ketosis shouldn’t be confused with Diabetic ketoacidosis, which can occur in type I diabetics when insulin and diet aren’t being well managed. This is a highly serious condition that needs urgent medical attention. If you have any concerns at all, it is best to work with a practitioner who is experienced in nutritional ketosis.
Some people are concerned at the extra cost of the extra food. If you are purchasing a whole-food diet, it’s likely that it won’t cost any more than your usual grocery bill. But you may have to invest in a few extra things that might not be in your cupboard, like a low-carb sweetener like erythritol or stevia) if you like making treats (like keto cheesecake- yum!).
Remember, it may take up to a month to adjust, and it can help to measure your ketone levels in the blood to get consistent results. It is quite a change for the body to shift metabolically from burning one source of fuel to another, so be gentle with yourself. There are heaps of recipes available online that are tasty and easy to prepare. Exercise can be a satisfying part of everyone’s life – moving our body is essential for good health, so make sure you are active, which can also support you moving to a ketogenic state.
Shop Ketogenic Supplements online now.